By Ava Malkin
Hydroquinone is a prescription-only topical ingredient used as a skin-lightening agent. It is often used as an active ingredient in dermatological medications aiming to target skin discoloration. Hydroquinone generally works to even out skin tone.
As the first pharmacy for sensitive skin, we offer various formulations with hydroquinone as an active ingredient dedicated to addressing melasma concerns.
Let’s analyze the uses of hydroquinone for melasma, highlighting the advantages of SKNV’s hydroquinone and exploring some field insights from our expert SKNV consultant.
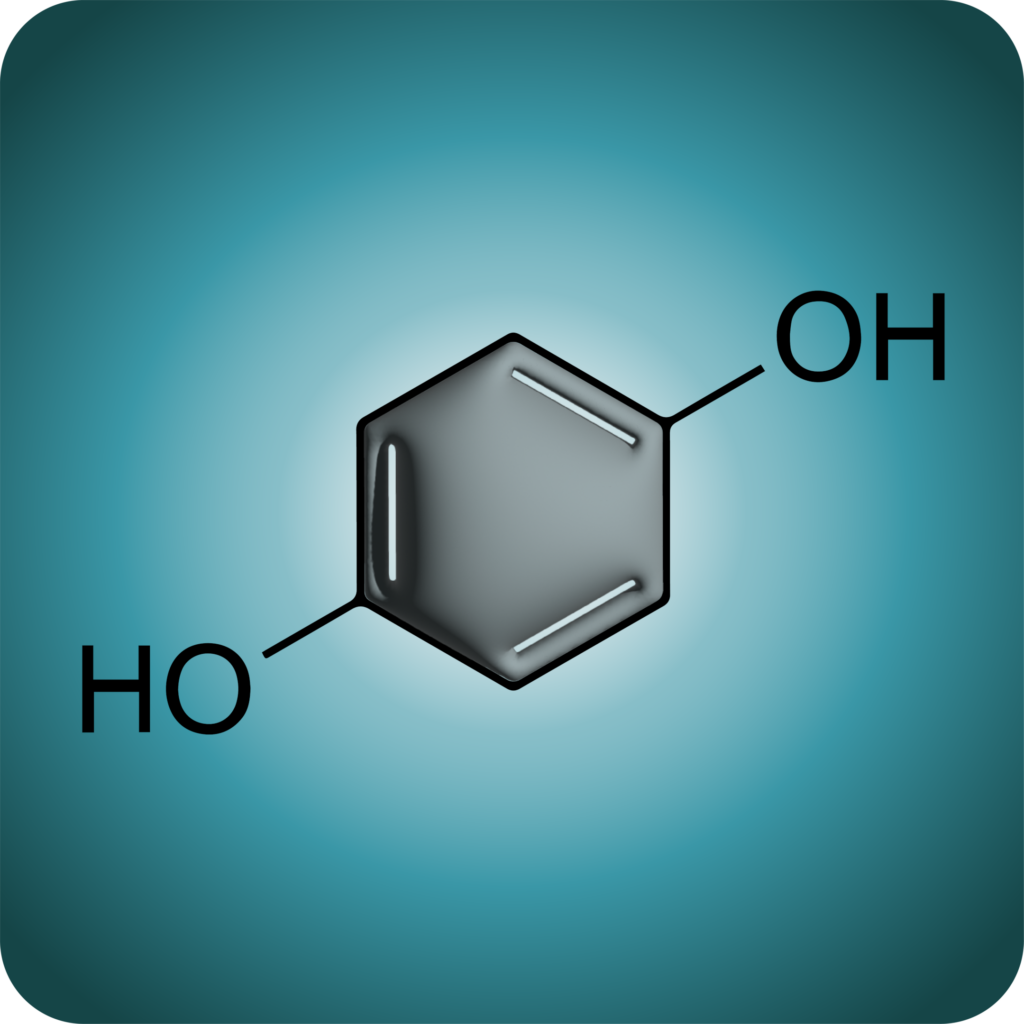
As previously mentioned, hydroquinone is a dermatological product that can lighten areas of the skin. It is used topically in various strengths/potencies and via different vehicles, including creams, emulsions, gels, lotions, and solutions. SKNV offers hydroquinone formulations in emulsion form, with potencies ranging from 4 to 8%.
Also formally known as dihydroxybenzene, hydroquinone is often called the “gold standard” of melasma treatment, as it is the most frequently prescribed depigmenting agent worldwide [1]. Beyond melasma, providers prescribe hydroquinone medications to target many skin conditions and concerns, including freckles, age spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation resulting from other skin diseases (e.g., acne or eczema).
Topical hydroquinone works to lighten dark spots and target uneven pigmentation by decreasing the number of melanocytes, the skin cells that produce melanin, our skin’s pigment. Maximum results may take time, as professionals often suggest hydroquinone treatment could take one month or more before the effects are visible [2].
Hydroquinone must be prescribed by a provider, as it cannot be bought over the counter. Although historically, a 2% hydroquinone concentration was available over the counter, the Food and Drug Administration has since required an official prescription for any potency of the skin-lightening agent [3].
Dermatological experts state that patients tend to tolerate hydroquinone treatment well. However, side effects are possible and should be monitored. Some side effects include dryness, itching, crusting, swelling, stinging, redness, general irritation, irritant contact dermatitis, and potentially even ochronosis (bluish-black pigmentation and bumps/pimples on the skin).
Despite the potential risk of adverse effects, dermatologist evaluations find topical hydroquinone to be safe [4, 5]. In fact, research has even indicated that hydroquinone therapy is useful in targeting post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation after acne [6] and melasma [7, 8, 9, 10].
In terms of how to apply a hydroquinone cream, emulsion, gel, lotion, or solution, you should use the topical medication as directed by your prescriber.
A general overview of the hydroquinone application procedure is as follows:
Wash your hands, and ensure the intended treated areas are clean and dry.
Apply a small amount of the medication gently and evenly on the affected areas. Avoid getting the medication inside the eyes, nose, mouth, or other sensitive areas.
Rewash your hands to prevent the hydroquinone from affecting other areas or bleaching materials.
If you notice one of the aforementioned side effects, if you recognize irritation or an allergic reaction to this topical use, if you are pregnant or trying to become pregnant, or if you are breastfeeding, contact your prescriber for an expert opinion about your hydroquinone usage and risk.
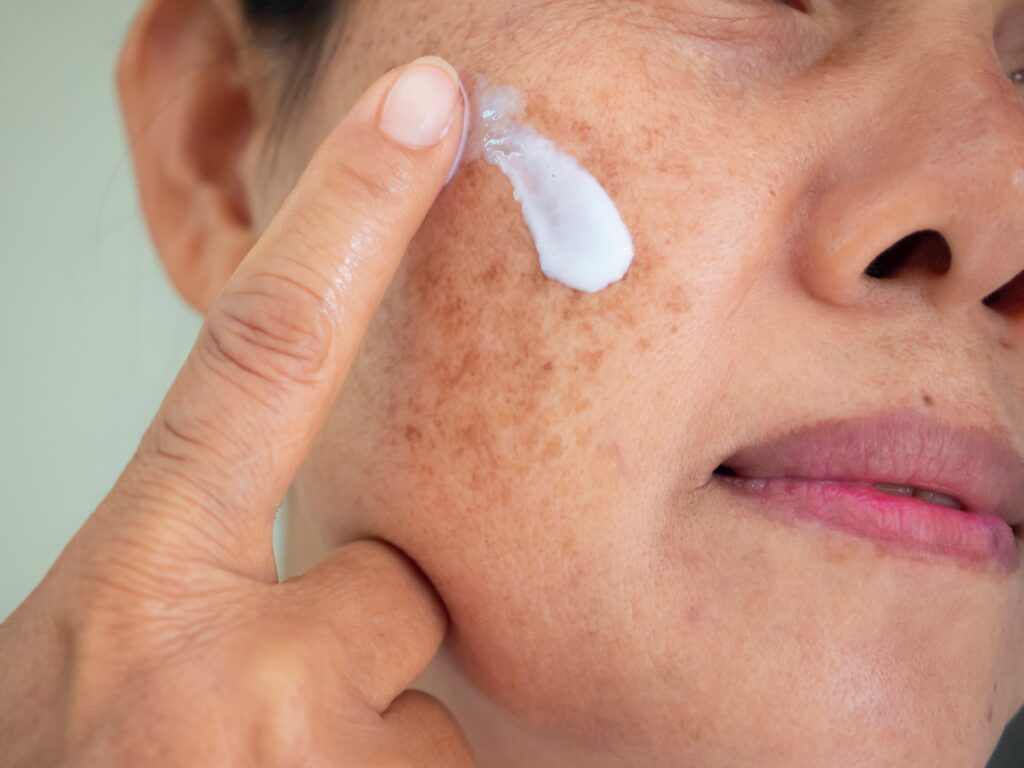
Hydroquinone is a standard treatment for melasma.
Melasma is a skin condition characterized by dark spots, or skin patches darker than one’s normal skin tone. It is most common among pregnant women, individuals with genetic predispositions, individuals with darker skin tones, individuals with thyroid disease, or those with intense sun exposure. Anyone experiencing the condition may seek out medication to target their pigmentation concerns [11].
Dermatologists often prescribe topical hydroquinone to help manage melasma, as this active ingredient works to decrease melanin production and mitigate uneven pigmentation.
Dermatology research has discovered that hyperpigmentation responds to hydroquinone therapy [7]. In combination with other active ingredients, hydroquinone medications prescribed to address melasma have been found to be safe and effective [9], showing more favorable responses than alternative treatments [12] and even yielding increased patient satisfaction [10].
Again, it is imperative to follow your dermatologist’s advice about using your hydroquinone prescription to target melasma; however, we can offer some practical tips on application and additional skin protection.
Do a patch test. Many professionals recommend a patch test area before treatment, where a small amount of the hydroquinone medication is applied to a specific area of the body that can be monitored for adverse effects, such as skin irritation (redness, mild itching, blisters, etc.) or an allergic reaction.
Use sunscreen. Dermatologists often suggest the use of a sunscreen with zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, or iron oxide to protect the skin from making more pigment, especially considering heightened sensitivity while using a hydroquinone medication [11].
Stay away from harmful sun rays. Avoidance of sun exposure (e.g., via protective clothing) and UV rays (e.g., via tanning beds/booths or sun tanning) is also recommended in combination with these medications. This aims to ensure that hyperpigmentation and other side effects are not worsened or amplified while using hydroquinone. [2]
Try to stay consistent. To yield the most benefit from your prescription and to remember to use your medication, apply the hydroquinone formulation consistently on the affected areas at the same time each day. Do not apply the melasma medication more often than directed by your dermatologist. If you miss a dose or forget to apply your medication, apply it as soon as possible, but do not double the next dose.
Wash your hands. As previously explained, it is important for the hands and skin to remain clean while applying a hydroquinone cream, emulsion, gel, lotion, or solution. Because hydroquinone is a lightening agent, washing hands after medication use will minimize the risk of bleaching clothes and other materials.
Beyond these insights into best practices for a skin regimen, it is also useful to know where one’s medication comes from. As an FDA-Registered 503B Outsourcing Facility, SKNV manufactures our medications under strict adherence to strict FDA regulation standards, state boards of pharmacy regulations, and Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP) to ensure the quality of our products; so, for high-quality hydroquinone formulations that underwent extensive testing, ask your provider for SKNV.

SKNV is an FDA-Registered 503B Outsourcing Facility. This means that we operate under section 503B of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act), which differentiates an outsourcing facility like ours from 503A Compounding Pharmacies.
503B Outsourcing Facilities must produce drugs under Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) requirements, adhering to both strict FDA regulations and state boards of pharmacy regulations. They do not require patient-specific prescriptions to formulate their medications, and their drugs can be manufactured in large batches.
For melasma medications specifically, being an FDA-Registered 503B Outsourcing Facility provides us with the unparalleled advantage of producing customized hydroquinone medications that are clinically different from branded treatments for certain patients who cannot tolerate commercially available drugs, as determined by their prescriber.
SKNV offers 23 melasma emulsions that contain hydroquinone as an active ingredient.

Unlike branded medications dedicated to targeting melasma, which only contain hydroquinone in a combination drug, SKNV offers melasma emulsions with hydroquinone alone. Our Kaxm Emulsion contains 4% hydroquinone, our Kexm Emulsion and Keido Emulsion contain 6% hydroquinone, and our Kuxm Emulsion and Kutea Emulsion contain 8% hydroquinone.
SKNV also offers hydroquinone formulations in combination with other active ingredients, including tretinoin, triamcinolone acetonide, and hydrocortisone. Additionally, we have hydroquinone medications with added inactive ingredients, such as kojic acid, upon providers’ request.
Many of our hydroquinone melasma formulations aim to eliminate certain inactive ingredient(s) that could be potential allergens or irritants for certain patients, as determined by the patient’s prescriber. We offer medications without inactive ingredients like trolamine, benzyl alcohol, alcohol, methylparaben, isopropyl myristate, isopropyl palmitate, propylene glycol, and mineral oil.
So, our hydroquinone medications target melasma by using quality ingredients and manufacturing practices, providing unique offerings and combinations, and maintaining a menu of tailored options to address an individual patient’s needs.

A patient may not be able to use hydroquinone if they experience adverse side effects, if they are allergic, if they are pregnant, if they are breastfeeding, if they have other skin conditions, or if they experience prolonged use (up to 6 months) with no results. When using hydroquinone is not an option, there are other skin-lightening methods to target skin discoloration and decrease melanin.
Some alternative melasma management options, aside from hydroquinone, include:

Other procedures: For more stubborn melasma, a board-certified dermatologist may suggest other skin-lightening measures, including chemical peels, microneedling, laser/light treatments, or plasma injection.
For these methods, ask your provider for SKNV anesthetics; our numbing creams and ointments, produced in our Florida FDA-Registered 503B Outsourcing Facility, aim to ensure the procedure is painless, and our pump minimizes contamination risk.
At SKNV, we are fortunate to have expert consultants who can share their insights on melasma in the field and how our hydroquinone medications function in practice.
We spoke with Rick Cocchi, our expert SKNV consultant who covers various regions of New York, including Long Island, Brooklyn, Queens, Staten Island, and the Bronx. Cocchi gave us an insider perspective on SKNV’s melasma formulations in his practices.
Cocchi noted that the most popular SKNV melasma medications in his practices are those that combine multiple active ingredients.
Consultants often say that providers tend to appreciate the freedom of prescribing various potencies of hydroquinone depending on a patient’s sensitivity, while also being able to combine active ingredients at such an affordable price point.
Cocchi sees this pattern with his providers, even explaining, “The melasma medications that I see prescribed most frequently are our Hydrocortisone/ Hydroquinone / retinoin with Kojic Acid formulations. These are most popular amongst providers because they are able to prescribe multiple active pharmaceutical ingredients in one easy to use bottle.”
While our combination medications might be the most popular, SKNV still offers a menu of melasma offerings to target each patient’s specific needs, as determined by the prescriber.
It is not uncommon for offices to use a multitude of our melasma offerings, which further contributes to SKNV’s goal of customizing our formulations to each individual patient.
This customization is beneficial to our consultants, their providers, and their patients.
“What I find most appealing about our melasma medications are the number of options available to providers and their patients. That is really what resonated with me when I started at SKNV,” Cocchi said. “I think Providers share a similar sentiment. They are excited to know that SKNV can facilitate a customized treatment plan for each individual patient in a compliant, affordable way.”
Cocchi noted that his practices find SKNV’s melasma formulations convenient in terms of prescribers’ desires and painless for patients’ wallets.
SKNV is unique because providers can select specific potencies tailored to a patient’s skin sensitivity, and their melasma does not necessarily have to be spot-treated only, our providers often say.
Our formulations make us stand out in the hydroquinone space, and we also take measures to ensure our medications are accessible and convenient.
“SKNV is unique in the sense that we can address many of the pain points within a practice. Issues like cost, medication substitutions and the ever-rising administrative burdens practices experience are at the forefront of many of our conversations in the field. Providers face many questions and it’s difficult for them to tell their patients the exact cost associated with their treatment,” Cocchi explaned. “With SKNV, there is no guesswork, no additional administrative burden. Providers have peace of mind knowing that they can select the exact medication they want to prescribe and are able to share with patients the cost upfront.”
With SKNV, we tailor our medications to patients’ needs (as determined by each prescriber for each patient) and mitigate insurance headaches to ensure the Rx process is convenient for both the provider and the patient.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site. By using our site, you consent to cookies.
Websites store cookies to enhance functionality and personalise your experience. You can manage your preferences, but blocking some cookies may impact site performance and services.
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Google Tag Manager simplifies the management of marketing tags on your website without code changes.
These cookies are used for managing login functionality on this website.
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us understand how visitors use our website.
Clarity is a web analytics service that tracks and reports website traffic.
Service URL: clarity.microsoft.com
SourceBuster is used by WooCommerce for order attribution based on user source.
Marketing cookies are used to follow visitors to websites. The intention is to show ads that are relevant and engaging to the individual user.
Facebook Pixel is a web analytics service that tracks and reports website traffic.
Service URL: www.facebook.com
LinkedIn Insight is a web analytics service that tracks and reports website traffic.
Service URL: www.linkedin.com
TikTok Pixel is a tracking tool that measures user interactions and optimizes ad campaigns on the TikTok platform.
Service URL: ads.tiktok.com
You can find more information in our Terms and Conditions and Terms and Conditions.